‘President Tinubu’s reforms are in the right direction’ – WTO
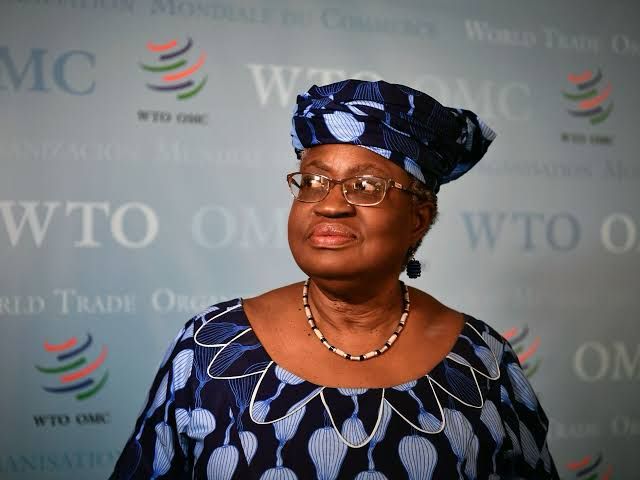

Nwali Chidozie Mrs. Ngozi Okonjo Iweala director of world trade organization (WTO) showered praises on the Nigerian president’s Bola Ahmed Tinubu led administration for sound economic policies, highlighting that the “reforms” has stabilized the economy of Africa’s most populous country. After a close door meeting with the president on Thursday, at the state house in Abuja, Nigeria’s capital; the former finance minister, told reporters that Nigeria is on the right path to economic growth and the administration’s “bold economic reforms” have been the pilot of this optimistic outlook. “The president and his team have worked out to stabilize the economy, and the reforms are in the right direction,” the WTO director said. Since president tinubu came into office in 2023 he embarked on controversial reforms which include: the removal of costly subsidies for premium motor spirit (PMS) mostly known as fuel, foreign exchange subsidies, electricity subsidies. These reforms, though also praised by the world bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF), did not sit well with many Nigerians – as they blame it for hardship, with many accusing the administration of using the “reforms” to push them into poverty. Mrs. okonjo however, noted that the discussions with the president was for “safety nets” to be implemented as soon as possible for the people whom the reforms have affected their businesses, and livelihood.
AU Backs a Campaign to End Use of Mercator Map

The African Union (AU) has officially thrown its support behind a campaign to replace the 16th-century Mercator map, a staple in classrooms and global institutions for centuries, in favor of projections that more accurately display Africa’s size. This move is part of a broader push to challenge historical biases and promote a more equitable representation of the world, as many see the map as a tool for colonialism. “It might seem to be just a map, but in reality, it is not,” AU Commission deputy chairperson Selma Malika Haddadi told Reuters. “The Mercator fostered a false impression that Africa was ‘marginal,’ despite being the world’s second-largest continent by area, with 54 nations and over a billion people.” The Mercator projection, while revolutionary for 16th-century sailors, severely distorts the size of landmasses near the poles, making countries like Greenland and Russia appear disproportionately large. This distortion minimizes the visual presence of Africa, a continent that is 14 times larger than Greenland. The campaign, titled “Correct The Map,” is led by advocacy groups Africa No Filter and Speak Up Africa. It promotes the Equal Earth projection, a 2018 map that correctly represents the relative sizes of all continents. “The current size of the map of Africa is wrong,” said Moky Makura, executive director of Africa No Filter. “It’s the world’s longest misinformation and disinformation campaign, and it just simply has to stop.” AU’s endorsement aligns with its goal of “reclaiming Africa’s rightful place on the global stage,” as Haddadi noted. The union will now advocate for wider adoption of more accurate maps and plans to promote the Equal Earth projection as the standard in African classrooms and global institutions.
NNPC Secures Court Victory, Spared from ₦5 Billion Damages

Nwali Chidozie The Nigerian National Petroleum Company (NNPC) Limited In a statement released on Wednesday, hailed the judgment of the court of appeal in Abuja as a landmark decision that spares the “company a massive financial payout and removes a significant legal risk that could have invalidated all board decisions made since 2021.” NNPC stated. Following legal battle stemmed from the removal of Senator Ifeanyi Araraume as the non-executive chairman of the NNPC board. The Court of Appeal in Abuja, overturning a lower court judgment that had previously awarded a staggering ₦5 billion in damages against the company. In September 2021, former President Muhammadu Buhari appointed Araraume to the board, but he was later replaced by Margaret Chuba Okadigbo in January 2022. Araraume, a former imo state senator representing Imo North, challenged his dismissal, arguing that it was wrongful and in violation of the Petroleum Industry Act (PIA) and the Companies and Allied Matters Act (CAMA). In April 2023, the Federal High Court in Abuja ruled in Araraume’s favor, declaring his removal unlawful, ordering his reinstatement, and awarding him ₦5 billion in damages for the disruption of his tenure. This judgment the NNPC argued created a significant legal and financial risk for the state owned company. NNPC swiftly filed an appeal, arguing that the Federal High Court’s decision was erroneous and that Araraume’s claim was “statute-barred,” meaning it was filed outside the legally prescribed time limit. The Court of Appeal’s judgment on August 8, 2025, sided with NNPC, agreeing that the lower court had erred in its ruling. The appellate court’s decision not only nullified the reinstatement of Araraume but, more critically for the state-owned oil firm, canceled the ₦5 billion in damages. NNPC, emphasized that the ruling secures governance stability, “establishes a crucial corporate governance precedent in Nigerian law, and upholds the validity of board resolutions critical for the oil and gas industry’s investment and policy direction.” NNPC noted.
Nigeria government prioritize capital budget execution to boost private sector
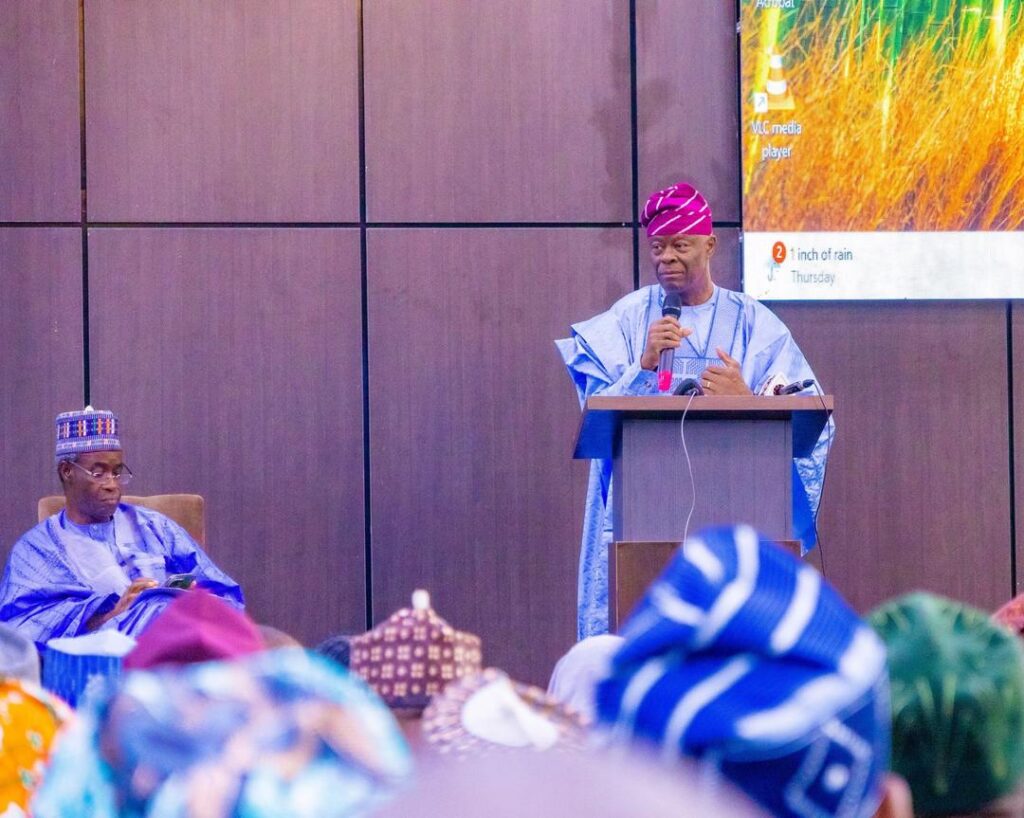

In a strategic move to stimulate economic growth and foster private sector confidence, the Nigerian Federal Government has announced significant reforms to the implementation of its 2025 capital budget. According to a statement on Wednesday from the Federal Ministry of Finance, the initiative, which is being spearheaded by the Minister of Finance and Coordinating Minister of the Economy, Mr. Wale Edun, aims to ensure transparent, efficient, and targeted spending to drive infrastructure development and achieve a targeted GDP growth rate of at least 7%. The reforms, which were the focus of a recent high-level meeting in Abuja, are designed to address historical challenges in budget execution and unlock the nation’s economic potential. A key component of the new framework is the integration of unspent 2024 capital funds into the 2025 budget through the Government Integrated Financial Management Information System (GIFMIS) platform. This measure is expected to streamline disbursements and ensure that all available funds are channeled into productive investments without delay. Meanwhile, under the revised framework is a strict requirement for Ministries, Departments, and Agencies (MDAs) to secure warrants before entering into any contracts. This measure directly links public expenditure with cash availability, reinforcing fiscal discipline and aligning spending with a “strict financial regulation” regime. This move is a departure from previous practices where contract awards sometimes outpaced actual funding, leading to payment delays and project abandonment. For the private sector, these changes are seen as a positive development. The reforms are expected to create a more predictable fiscal environment, which is a crucial factor for investment decisions. “Nigeria’s future growth depends on effective, honest, and targeted spending,” Minister Edun stated. “We must ensure that public resources work harder for our people and our economy.” He added. The World Bank has long highlighted the need for Nigeria to improve its non-oil revenue base and public financial management systems to achieve sustainable growth. This new emphasis on capital budget execution aligns with the government’s broader economic strategy, which includes attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) and improving the ease of doing business. With these reforms, the Nigerian government is poised to unlock its economic potential and drive sustainable growth. By prioritizing transparent and efficient budget execution, it is sending a clear message to investors and citizens alike: that it is committed to building a better and more prosperous future for all Nigerians.
‘Give us loans’ – Kenya to IMF

Nwali Chidozie Kenya is seeking a funded program from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), according to the country’s central bank governor, Kamau Thugge. The announcement comes on Wednesday ahead of a scheduled IMF visit next month, where a new program request will be discussed. The East African country and the IMF had previously agreed to a new lending program earlier this year, after walking away from the final review of a prior arrangement. Finance Minister John Mbadi had stated that the new program was requested to account for unused funds from the previous facility, which had around $800 million remaining. The shift to a “funded” program indicates Kenya’s desire for a new agreement that provides financial disbursements, as opposed to a non-funded one which focuses on policy advice and monitoring. An IMF delegation is expected in Nairobi in September for an Article IV consultation, a regular economic health check for member countries. The visit will also serve as the platform for formal discussions on the new funding program. The request for a new program follows a period of economic challenges for Kenya, including a high debt burden and the need to balance fiscal tightening with the public’s demands for social spending. Meanwhile, previous IMF-backed measures, such as new tax proposals, have faced public opposition and protests. The outcome of the upcoming discussions will be critical for Kenya’s economic trajectory in the months ahead, as the government seeks to secure much-needed funding while navigating domestic political and social pressures.
Wale Edun Commends Lotus Capital’s Leadership in Non-Interest Finance
The Honourable Minister of Finance and Coordinating Minister of the Economy, Mr. Wale Edun, has praised Lotus Capital Limited for its pivotal role in advancing non-interest finance in Nigeria. He highlighted the necessity of public-private partnerships to attract long-term, sustainable capital for national development. According to a press release from the Federal Ministry of Finance on Tuesday, Edun “emphasised that collaboration between the public and private sectors will be essential to mobilising sustainable, long-term capital for national development.” Lotus Capital Limited is a full-service ethical investment management company specializing in Asset Management, Private Wealth Management, and Financial Advisory services. The company is also a pioneer in non-interest finance in Nigeria with a BBB+ rating and stable outlook from Agusto & co credit rating agency. The minister noted several key initiatives, including the potential for a Non-Interest Real Estate Investment Fund and a consistent sovereign sukuk issuance program. These initiatives, Edun notes, could “attract ethical investment into critical infrastructure, boost market liquidity, and widen access to finance for under-served communities.” The Ministry’s engagement with Lotus Capital underscores its commitment to exploring innovative financing solutions to spur economic growth and development. The meeting highlighted the “importance of public-private partnerships in driving progress in the non-interest finance sector,” the statement from the Ministry affirmed.
AI Startup Perplexity Offers $34.5 Billion for Google’s Chrome Browser

AI startup Perplexity made an unsolicited all-cash offer of $34.5 billion to acquire Google’s Chrome web browser on Tuesday. The bid comes at a critical time for Google, which is facing intense regulatory pressure and a potential court-ordered divestiture of Chrome following a U.S. antitrust ruling. The offer, made to Google parent company Alphabet, is more than double Perplexity’s own reported valuation of approximately $18 billion. Perplexity CEO Aravind Srinivas has stated that the acquisition is “designed to satisfy an antitrust remedy in highest public interest by placing Chrome with a capable, independent operator.” The San Francisco based startup proposal is not just about the price tag. The company has outlined a series of commitments aimed at easing concerns from both regulators and users. These include a pledge to invest $3 billion over two years in Chrome’s development, keeping the underlying Chromium code open-source, and, crucially, maintaining Google as the default search engine within Chrome while still allowing users to change it. The timing of the offer is no coincidence. A federal judge previously ruled that Google holds an illegal monopoly in internet search, and a decision on a potential remedy, including the forced sale of Chrome, is expected soon. While Google has not yet publicly responded to the offer, analysts believe a sale is highly unlikely without a prolonged legal battle. Google has consistently pushed back against the idea of selling Chrome, arguing that it would harm its business and could even pose a risk to national security.
Nigeria’s Oil Production Surpasses OPEC Quota in July

Lagos, August 12 — Nigeria’s crude oil production witnessed a significant increase in July, surpassing the nation’s OPEC quota for the second consecutive month and providing a major boost to the country’s economic aspirations. The improved output, largely credited to enhanced security measures and a new production drive, is seen as a positive step toward meeting the ambitious targets set in the 2025 national budget. According to figures released by the Nigerian Upstream Petroleum Regulatory Commission (NUPRC), Nigeria achieved a peak daily production of over 1.8 million barrels per day (bpd) in July, with an average daily output hovering around 1.78 million bpd. Similarly, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), in its latest Monthly Oil Market Report released on Tuesday, also confirmed Nigeria’s strong performance. OPEC’s data, based on direct communication with Nigerian authorities, reported an average daily production of 1.507 million bpd for July, a slight increase from the 1.505 million bpd recorded in June. Both figures place Nigeria comfortably above its OPEC quota of 1.5 million bpd. A Push for Increased Output The Commission Chief Executive of the NUPRC, Gbenga Komolafe, speaking at the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE) Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition (NAICE) in Lagos, attributed the gains to the “Project 1 MMBOPD Incremental initiative.” This multi-stakeholder approach focuses on minimizing production disruptions, optimizing the Maximum Efficient Rate (MER) framework, and aligning operational shutdowns to maintain steady output. The increase in production is also a direct result of intensified security operations in the Niger Delta, which have significantly reduced instances of crude oil theft and pipeline vandalism. For years, these challenges, coupled with underinvestment, had severely hampered Nigeria’s ability to meet its production targets, straining public finances and foreign exchange earnings.
Musk Accuses Apple of Favoring OpenAI, Threatens Legal Action

World richest man Elon Musk has renewed his feud with Apple, accusing the tech giant of anti-competitive behavior and threatening legal action. In a series of posts on his social media platform X, Musk alleged that Apple’s App Store unfairly favors OpenAI, making it “impossible” for other AI companies to reach the top ranks. Musk’s criticism comes after Apple’s highly publicized partnership with OpenAI, which integrates ChatGPT into Apple Intelligence across its devices. Musk claims this partnership has led to preferential treatment for OpenAI’s app in the App Store, an “unequivocal antitrust violation.” He specifically pointed to the fact that his own companies’ apps, X and the Grok AI chatbot, are not being featured in the App Store’s “Must Have” section despite their high rankings in other categories. In response, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman fired back at Musk, accusing him of hypocrisy. Altman suggested that Musk’s claims were disingenuous, citing reports that Musk has manipulated the algorithm on his own platform, X, to benefit his personal interests and companies while harming competitors. While Apple has yet to issue an official response to Musk’s allegations, the threat of legal action and the public back-and-forth between the tech titans underscore the heated competition and regulatory challenges in the rapidly evolving AI landscape.
South Africa’s Unemployment Rate Rises to 33.2% in Second Quarter, Data Shows

South Africa’s official unemployment rate climbed for the second consecutive quarter, reaching 33.2% in the April-June period of 2025, according to data released on Tuesday by Statistics South Africa (Stats SA). The new figure represents a 0.3 percentage point increase from the 32.9% recorded in the first quarter of the year. The latest Quarterly Labour Force Survey (QLFS) paints a challenging picture of the country’s job market. While the number of employed people saw a modest increase of 19,000 to 16.8 million, this was overshadowed by a substantial rise in the number of unemployed individuals. The number of jobless people grew by 140,000, bringing the total to approximately 8.4 million. This means that while 159,000 more people entered the workforce between April and June, only a fraction of them found employment. Meanwhile, the data also highlighted persistent disparities within the labor market. The unemployment rate for women stood at 35.9%, compared to 31.0% for men. This gender gap is even more pronounced among those with lower educational qualifications. Youth unemployment remains a particularly acute issue, with the rate for individuals aged 15-24 soaring to 62.4%. This indicates a decade of deteriorating job prospects for millions of young South Africans. Despite the increase in the official unemployment rate, the expanded definition of unemployment, which includes discouraged job seekers, saw a slight decrease to 42.9% from 43.1% in the previous quarter. suggesting a marginal decrease in the number of people who have given up looking for work. Gains were primarily observed in the formal sector (up by 34,000 jobs) and private households (up by 28,000). However, these gains were offset by significant job losses in community and social services (42,000 jobs), as well as finance and agriculture (24,000 jobs each). The new statistics come just days after the implementation of a 30% tariff by the United States on South African goods, a measure expected to further impact key industries such as agriculture, vehicle manufacturing, and steel, potentially exacerbating the country’s employment challenges.


